Difference between revisions of "VHDL tutorial"
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
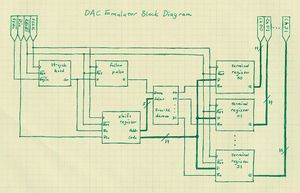
=== Example: the block diagram === | === Example: the block diagram === | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[Image:DAC_Emulator_Block.JPG|thumb|Functional block diagram of the DAC emulator.]] |
The block diagram is shown to the right, and each block is described on the [[http://zeus.phys.uconn.edu/wiki/index.php?title=Programming_the_FPGA#Emulator_.28D.29|FPGA programming page]]. | The block diagram is shown to the right, and each block is described on the [[http://zeus.phys.uconn.edu/wiki/index.php?title=Programming_the_FPGA#Emulator_.28D.29|FPGA programming page]]. | ||
Revision as of 15:24, 6 July 2007
FPGA programming using a hardware description language is not a commonly taught skill in physics programs, but is a necessary skill for designing the electronics required for this project. This tutorial aims to layout the design process and teach the basics of hardware description language; in particular VHDL. The main competitor to VHDL is Verilog; tutorials and information regarding Verilog can be found through Google web searching.
Design example
To illustrate the discussions in this tutorial, a design example is discussed along the way. The design example is the [for the AD5535 DAC]. As each step of the design process is discussed, the DAC emulator will be used for illustration.
Where to start
The black box
The first part of the design process is completely independent of any code. The first step is to define the "black box" of your circuit; that is, draw a box and say what goes in and what comes out. VHDL allows three types of pins (connections to the outside world):
- in: An in pin can be read from but never written to.
- out: An out pin can be written to but never read from.
- inout: An inout pin can be both read from and written to, providing the flexibility to allow bidirectional communication on a single line. At first this seems the ideal choice and that you would always want inout pins; in actual fact you want to avoid inout pins unless you absolutely need them for bidirectional communication.
Some notes on nomenclature and notation:
- The term signal is sometimes used to generically refer to a line, pin, or bus.
- Signals come in active-high and active-low varieties. Active-high means that a logical 1 is "on" and a logical 0 is "off". It is also known as "positive logic". Active-low is the exact opposite; logical 0 is "on" and logical 1 is "off", and it is alternately known as "negative logic".
- Some signals serve double-duty. As active-high logic they perform one operation, but as active-low logic they perform another operation. This links these operations as complimentary pairs. For example a shift register may shift its output or it may load a new value. If it's not shifting then it's loading. So the name would be something like "Shift/Load" to signify that shifting is active-high and loading is active-low. Carrying over this notation, any signal that is written "/Name" is an active-low signal. This notation is not always used, but it is quite common and I shall attempt to maintain this practice throughout the tutorial. When writing on paper, an active-low signal is frequently denoted by an overbar instead of a leading slash. Unless otherwise specified, a signal that is not marked as active-low is assumed to be active-high by default. Some designs assume active-low as the default, but that will either be marked or implied by context (i.e. all active-high lines marked as such).
- A pin is an input, output, or inout. A line is a single pin or a single bit of data flowing along a wire. A bus is properly a multidrop line, but through common usage (due to the way circuits are commonly designed), in digital logic at this level the term has come to mean multiple lines bound together into a bundle. On a diagram, a bus appears as a thick line with a slash through it. Near the slash will be a number denoting how many lines are bundled into that bus.
Example: the block box
For the DAC emulator, the inputs are clearly defined for us. The AD5535 data sheet discusses the [interface protocol] in detail. We need four input lines:
- /Reset: an asynchronous, active-low reset line
- D_in: serial data line
- /Sync: an active-low flag to being transmission
- SClk: a serial clock
Our outputs are not so clearly defined. This emulates the circuit itself, so the output of the black box is purely for our benefit to aid in testing. So I decided to define as outputs 32 channels, each 14-bits wide, which display the value being fed to each DAC at any given time.
The block diagram
Having defined your block box, you need to fill in your black box. But before doing that, we need to note the different between two types of logic:
- Combinational logic merely recombines lines into new lines. For example, signal Q may be the logical AND of signals A, B, and C. There is no reference to a clock in combinational logic.
- Sequential logic is any logic that makes use of a clock for latches, flip-flops, registers, or other devices. Sequential logic changes only when the clock changes. Often circuits are wired so that all sequential logic changes together, either on a falling edge of a clock or a rising edge of a clock. Advanced designs can change some components on a rising edge and other components on a falling edge, but this is significantly more difficult due to the tighter timing restrictions imposed.
A "good" design does its best to separate combinational and sequential logic. All combinational logic takes time; each gate has a delay associated with it. Highly complex combinational logic can take long enough to skew the timing of your circuit; some lines will clock in too late and will take effect on the following clock cycle, completely ruining your synchronization and causing sporadic or faulty behavior in your circuit. For this reason it is best to separate the two types of logic as best you can, although it is not always possible to fully separate them. Generally the sequential block will feed the combinational block, and the combinational block will loop back to the sequential block for any required feedback or recursion.
Bearing this in mind, you need to partition your design into functional blocks. Each functional block will be a new black box within the larger design, with two well-defined attributes: I/O pins and functionality. Sometimes these functional block diagrams will become layered, with a functional block in the top-most diagram having a functional block diagram describing its own internals. For complex designs, there can be many layers and many engineers, so that each engineer is only working on a small subset of the components so that the I/O ports and functionality must be precisely defined and followed so that integration of the components requires a minimum of component redesign. The functional block diagram shows the I/O ports of the overall design (if you have no inouts, it is conventional to put inputs on the left and outputs on the right at all times to clarify data flow), all blocks (with I/O ports labeled), and signals connecting each block as appropriate.
Notes:
- Since clock lines are required for most designs (every sequential block needs one), most engineers no longer write the world "clock" or even the abbreviation "CLK" on a block diagram. Instead it is understood that a clock line is represented by a small carat or divot on the side of the block (often placed in the top left corner of the block, but that is not a requirement).
- Many devices are general purpose, so giving a descriptive label to a pin would be pointless as the description will change depending on the application. A common shorthand for such blocks is to use "D" as the input signal and "Q" as the output signal. This is often seen on registers, multiplexers, flip-flops, etc.
Example: the block diagram
The block diagram is shown to the right, and each block is described on the [programming page].
VHDL Resolution Table
| U | X | 0 | 1 | Z | W | L | H | - | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U |
| X | U | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 0 | U | X | 0 | X | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | X |
| 1 | U | X | X | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | X |
| Z | U | X | 0 | 1 | Z | W | L | H | X |
| W | U | X | 0 | 1 | W | W | W | W | X |
| L | U | X | 0 | 1 | L | W | L | W | X |
| H | U | X | 0 | 1 | H | W | W | H | X |
| - | U | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
VHDL Logic States
- U: uninitialized
- X: forcing unknown
- 0: forcing 0
- 1: forcing 1
- Z: high impedance
- W: weak unknown
- L: weak 0
- H: weak 1
- -: don't care