

Next: Single shower fitter
Up: psf
Previous: psf
Current mechanism for reconstructing photon showers, their energy, position,
and multiplicity in the LGD is based on the IU clusterizer.
One of the factors that limits the clusterizer efficiency in reconstructing
showers from the hits in the LGD is the finite size of the LGD blocks (4x4 cm). Showers separated by less than
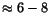
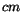 are very hard to
distinguish. In addition, low energy photons can escape from the eye
of the clusterizer, and can be merged into a high-energy neighbor. From
previous study [1] it is realized that accurate photon multiplicity
reconstruction is crucial for eliminating background from the final states
of interest to Radphi.
One approach to improve shower reconstruction is to exploit the shape of
the shower in the LGD, depending on the photon energy and impact angle.
The idea is based on the optical imaging technique, used for example
in astrophysics, to reconstruct the point light source from the known
response function in the detector, called the point spread function (PSF).
The procedure to build a new algorithm should be as follows:
are very hard to
distinguish. In addition, low energy photons can escape from the eye
of the clusterizer, and can be merged into a high-energy neighbor. From
previous study [1] it is realized that accurate photon multiplicity
reconstruction is crucial for eliminating background from the final states
of interest to Radphi.
One approach to improve shower reconstruction is to exploit the shape of
the shower in the LGD, depending on the photon energy and impact angle.
The idea is based on the optical imaging technique, used for example
in astrophysics, to reconstruct the point light source from the known
response function in the detector, called the point spread function (PSF).
The procedure to build a new algorithm should be as follows:
- 1
- - use isolated showers to guess the shower shape and make a 1-cluster
fitter based on the PSF that will depend only on the shower energy
and position
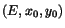 .
.
- 2
- - obtain a good sample of isolated clusters from real data, and modify
the PSF as necessary. Compare resolution and efficiency with the current
clusterizer.
- 3
- - design a multi-cluster fitter using MC data and refine on real data.
Make decision regarding further analysis based on the comparison
with the current clusterizer.


Next: Single shower fitter
Up: psf
Previous: psf
Richard T. Jones
2004-04-30